Emu
Dromaius novaehollandiae
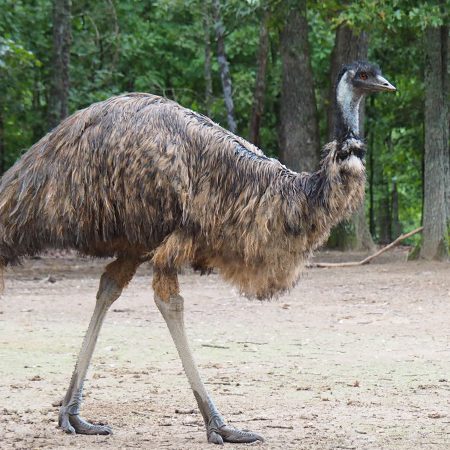
The emu is the second-largest living bird by height. Emus belong to a group of flightless running birds known as ratites. It is endemic to Australia where it is the largest native bird and the only extant member of the genus Dromaius. The emu's range covers most of mainland Australia.
Emus are soft-feathered, brown, flightless birds with long necks and legs, and can reach up to 6.2 ft in height. Emus can travel great distances, and when necessary can sprint at 31 mph. They are omnivores and forage for a variety of plants depending on the season, springtime brings insects and fruit. Emus have also been known to go for weeks without eating and will drink infrequently, but take in copious amounts of water when the opportunity arises.
The emu has a pouch in its throat that is part of the bird's windpipe and is used for communication. When the pouch is inflated, the emu can make deep booming, drumming, and grunting sounds. These calls are usually made during courtship and the breeding season, heard up to 1.2 miles (2 kilometers) away! A hiss, described by one of our animal trainers as bloodcurdling, is effective at warning off dingoes.
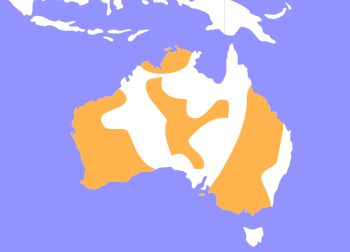
Emus are native to the drylands of Australia.
HABITAT -They most commonly inhabit areas of savannah woodland and forest in less heavily populated districts.
DIET -Emus are omnivorous, eating fruits, seeds, shoots, plants and insects.
FUN FACT -Emus swallow small stones, called gastroliths, which stay in the gizzard and help grind up food.
SOCIAL BEHAVIOR -They are generally docile, occasionally fighting amongst themselves. They can also be considered curious.
ACTIVITY -They are diurnal being most active during the day and resting during the evening.
PREDATORS -Predators include the dingo, wedge-tailed eagle, and goanna.
SIZE -Length averages 5.7 ft, weighing between 79 - 88 lbs.
RELATIVES -Relatives include other flightless birds of the ratite family, such as the ostrich and rhea.
CONSERVATION -Emus are categorized as LC (Least Concern) species by the IUCN.
Cub Creek Animal Care Information
Housing - Our emus thrive in open pasture environments, with lush green fields for grazing. The pastures are enclosed with fencing to keep predators out, and provide a covered area to take shelter in extreme weather. We provide automatic water dispensers that always keep fresh water. The back of their pasture has a strip of trees which they use to make nests and lay eggs.
Diet - They are fed a mixture of game bird finisher and cracked corn to make sure they get all the necessary nutrients and vitamins. They also have access to a Nelson water bowl, which constantly provides them with fresh water.
Enrichment - Living in a multi-species enclosure gives our emus lots of enrichment through daily interactions. We also will occasionally scatter feed, which prolongs eating time by making them seek out their food instead of just having it in one location.


