Kinkajou
Potos flavus
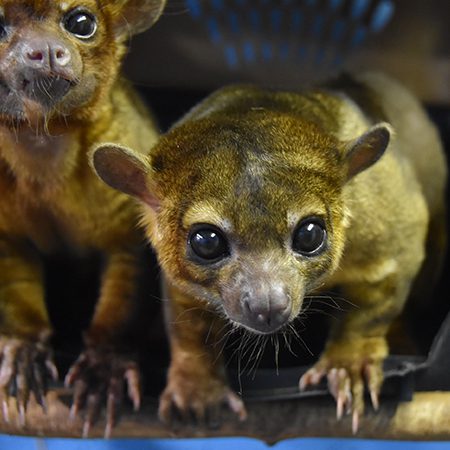
Kinkajous are known as the “honey bear” of Central and South America. They are arboreal, living the majority of their lives in the trees. Although they have evolved to live this lifestyle, they are not closely related to other tree-dwelling mammals such as primates. This tropical rainforest mammal is part of the family Procyonidae, the same family as raccoons. Kinkajous range from east and south of the Sierra Madres in Mexico, throughout Central America to Bolivia east of the Andes and southern Brazil. These animals are nocturnal, with its peak activity occurring during the evening. During daylight hours, kinkajous sleep in tree hollows or shaded tangles of leaves.
Kinkajou are classified in the order Carnivora and has sharp teeth, with its omnivorous diet consisting mainly of fruit. They are also equipped with a prehensile tail and dexterous sharp claws that make hanging from the trees to grab fruit even easier! Kinkajous have a slender five-inch tongue that assists in obtaining fruit and to lick nectar from flowers. When eating softer fruits they hold it with their forepaws, then scoop out the succulent pulp with their tongue! In the wild this plays an important role in seed dispersal, scattering fruit seeds among the tropical forest floors.
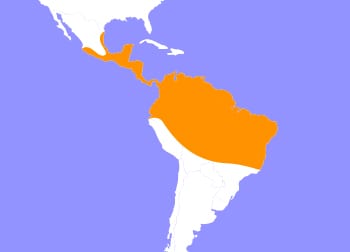
Kinkajous range from the Sierra Madres in Mexico, throughout the tropical rainforests in South America.
HABITAT -They inhabit the tropical forests and lowland forest of Central and South America.
DIET -Omnivorous diet that consists of mainly fruit, like figs.
FUN FACT -Kinkajous have a prehensile tail or “fifth arm” that assists them in climbing.
SOCIAL BEHAVIOR -Usually solitary but will occasionally forage in small groups.
ACTIVITY -They are nocturnal, meaning they're mainly active at night and rest during the day.
PREDATORS -Main predators are foxes, tayra, jaguars, ocelot, and deforestation by humans.
SIZE -Adult kinkajous weigh around 3 - 10 lbs.
RELATIVES -They are part of the Procyonidae family related to coatis, raccoons, and olingos.
CONSERVATION -Kinkajous are categorized as LC (Least Concern) species by the IUCN.
Cub Creek Animal Care Information
Housing - Our Kinkajous are housed in large enclosures with plenty of trees and hides to explore. They are amazing climbers, being able to scurry all around tree limbs on the ceiling to create a more natural environment. Their indoor enclosure is bedded with shavings, while the outdoors is bare ground.
Diet - Just like in the wild, their diet consists of mainly fruit! They love a good mixture of apples and bananas mixed with some fruit yogurt, or the occasional mango or other sweet treat.Their diet is supplemented with a food mixture that meets the high-protein, high-energy needs.
Enrichment - We provide our Kinkajous with plenty of enrichment to keep them stimulated and healthy. Our kinkajous are accustomed to human interaction, leaping onto shoulders being quite docile in nature. This stems from continual enrichment with toys and social interaction. During the summer, campers will make all kinds of toys for them, made out of cardboard and other materials!.


